|
Welcome
to Frank Yang Lab Web
Page |
The Frank Yang laboratory focuses on bacterial
pathogenesis—how bacterial pathogens colonize the host, evade host immune
response and cause diseases. The ultimate goals are to develop new diagnostic
tools and vaccine to detect and prevent infections.
The primary focus of The Frank Yang Lab revolves
around researching the pathogenesis of Lyme disease. As the leading
vector-borne disease in the United States, Lyme disease poses a significant
health concern. However, the understanding of how the causative agent, Borrelia
burgdorferi, induces various manifestations such as Lyme arthritis, Lyme
carditis, and neuroborreliosis remains limited. Presently, there is a notable absence
of a human vaccine for preventing Lyme disease, and the diagnostic capabilities
are suboptimal.
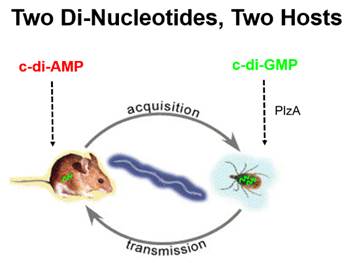 One area of the Lyme disease research is to elucidate the
strategies B. burgdorferi employs that allow the pathogen to survive in
the mammalian host and the tick vector. The laboratory has identified two key
regulatory networks (Hk2-Rrp2, Hk1-Rrp1) and two di-nucleotide secondary
messengers (c-di-GMP, c-di-AMP), that are essential either for the pathogen to
infect mice or to survive in the tick vector. These pathways control many
differentially expressed genes, and are potential targets for vaccine candidate or for diagnosis development.
One area of the Lyme disease research is to elucidate the
strategies B. burgdorferi employs that allow the pathogen to survive in
the mammalian host and the tick vector. The laboratory has identified two key
regulatory networks (Hk2-Rrp2, Hk1-Rrp1) and two di-nucleotide secondary
messengers (c-di-GMP, c-di-AMP), that are essential either for the pathogen to
infect mice or to survive in the tick vector. These pathways control many
differentially expressed genes, and are potential targets for vaccine candidate or for diagnosis development.
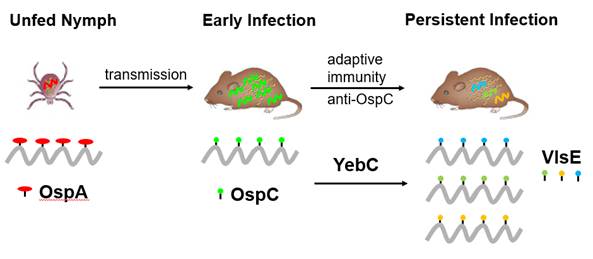 Another area of the Lyme disease research is to study the mechanism of immune
evasion by B. burgdorferi for its persistent infection.
Differential expression of VlsE that undergoes antigenic variation is a key
immune evasion strategy employed by B. burgdorferi. vlsE expression
increases concomitantly with downregulation of the major immunodominant surface
lipoprotein OspC in response to host adaptive immune response activation. The
laboratory discovered a key transcription factor, YebC, that regulates vlsE
expression. This finding sets the foundation to study how the pathogen senses
the immune pressure to activate the VlsE antigenic variation system and
provides a potential therapeutic target to combat persistent Lyme disease.
Another area of the Lyme disease research is to study the mechanism of immune
evasion by B. burgdorferi for its persistent infection.
Differential expression of VlsE that undergoes antigenic variation is a key
immune evasion strategy employed by B. burgdorferi. vlsE expression
increases concomitantly with downregulation of the major immunodominant surface
lipoprotein OspC in response to host adaptive immune response activation. The
laboratory discovered a key transcription factor, YebC, that regulates vlsE
expression. This finding sets the foundation to study how the pathogen senses
the immune pressure to activate the VlsE antigenic variation system and
provides a potential therapeutic target to combat persistent Lyme disease.
In
addition to Lyme disease, the Frank Yang Lab also works on identification of
factors as potential candidates for diagnosis and vaccine development against
Syphilis (one of the important sexual transmitted infections caused byTreponema pallidum) and Leptospirosis
(a re-emerging zoonotic disease caused by Leptospira interrogans).
Current
Research Funding
5R01,
AI083640 (Yang), 6/2023-5/2028
Regulatory
Network of the Lyme Disease Pathogen
R01AI152235 (Yang, Sintim)
6/2020-5/2025
Targeting Cyclic Dinucleotide Signaling
Pathways to Interrupt the Nature Cycle of Borrelia burgdorferi
R21,
NIH-NIAID AI169333-01A1 (Yang) 5/2022–
4/2024
The
Role of YebC in persistent infection of the Lyme disease pathogen
Steven & Alexandra Cohen Foundation
(Yang, Sintim) 5/2020-4/2024
Development of Novel Therapeutic Compounds
against Active
and Persistent Borrelia burgdorferi
Selected
Publications
1.
Alazani
F, Ranghunandanan S, Priya R, Yang XF*. 2023.
The RpoN-RpoS regulatory pathway plays an important
role in the blood-brain barrier transmigration of the Lyme disease pathogen. Infection
and Immunity. 91(11):1-12, e0022723. doi:
10.1128/iai.00227-23.
2.
Priya, R.,
Raghunandanan, S., Alanazi, F. and Yang XF*. 2023. Borrelia burgdorferic-di-AMP
induces type I IFN response in macrophage through the activation of STING
signaling pathway. The Journal of
Immunology, 210,
241.207.
3.
Zhang
Y, Chen T, Raghunandanan S, Xiang X, Yang J, Liu Q, Edmondson DG, Norris S, Yang
XF*, Lou Y*. 2020. YebC regulates variable surface antigen VlsE expression
and is required for host immune evasion in Borrelia burgdorferi. PLOS
pathogens. 16(10), e1008953. doi:
10.1371/journal.ppat.1008953.
4.
Zhang
JJ, Yang Y, Troxell B, He M, Carrasco S, Du J, Li H, Gomelsky
M, Yang XF*. 2018. Dual Roles of
c-di-GMP Binding Protein PlzA in the Regulation of
Glycerol Uptake and Metabolism in Borrelia
burgdorferi. Journal of Bacteriology. 200 (22) e00243-18; DOI:
10.1128/JB.00243-18
5.
Zhang
JJ, Hu WL, Yang YY, Picardeau M, Yan J, Yang XF*. 2018. The sigma factor σ54
is required for the long-term survival of Leptospira
biflexia in water. Molecular Microbiology.
109(1): 63-77. PMID: 29633391; DOI: 10.1111/mmi.13967
6.
Radolf JD, Deka RK, Anand A, Šmajs D, Norgard MV, Yang XF. 2016. Treponema pallidum, the syphilis spirochete: making a living as a
stealth pathogen. Nature Review Microbiology.
14(12):744-759.
7.
Chou
S, Daugherty M, Peterson S, Biboy J, Yang Y, Jutras B, Fritz-Laylin
L, Ferrin M, Harding B, Jacobs-Wagner C, Yang
XF, Malik H, Vollmer W, Mougous J. 2015.
Transferred interbacterial antagonism genes augment eukaryotic innate immune
function. Nature. 518(7537):98-101. PMCID:PMC4713192
8.
Troxell
B, Xu H, Yang XF*. 2012. Borrelia burgdorferi, a pathogen that
lacks iron, encodes a Mn-dependent superoxide dismutase that is required for
resistance to streptonigrin. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 287(23):19284-93.
9.
He
M, Ouyang Z, Troxell B, Xu H, Moh A, Norgard M, Piesman
J, Gomelsky, M, Yang XF*. 2011. c-di-GMP is essential for the enzootic cycle of Borrelia burgdorferi. PLoS
Pathogens. 7(6): e1002133
10.
Xu
H, Caimano M, Lin T, He M, Radolf
J, Norris S, Gherardini F, Wolfe A, Yang XF*.
2010. Role of acetyl-phosphate in activation of the Rrp2-RpoN-RpoS
pathway in Borrelia burgdorferi.
PLoS Pathogens. 6(9): e1001104.
doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1001104
Click here for a full list of publications in PubMed
Research
Team
Sajith Raghunandanan, Ph.D., Postdoc Fellow
Raj Priya, Ph.D., Postdoc Fellow
Gaofeng Lin, Ph.D., Research
Scientist
Fuad Alazani, Ph.D. Candidate
Elise Warren, BS, Research Technician



